

This could provide opportunities for expansion, new equipment, or a new project, like starting a delivery service to local offices, for example. Since our coffee shop example is easily capable of meeting it’s short-term debts, it’s excess working capital could be invested into the business’ future. They have enough current assets to cover their debts. If a business’ current assets are greater than current liabilities, this indicates that the risk that they won’t be able to pay short-term debts is low. The value of this coffee shop’s current assets are greater than their current liabilities.īut what does this mean exactly, and what can they do now? If we look at the example from the previous section. What does it mean to have a positive working capital?
#Should your working capital turnover ratio be negative how to#
For example, a ski rental shop will have much greater working capital in their high season vs their low season.įind out more: How to fix off-season cash flow woes It’s important to realise that working capital can fluctuate depending on the season and industry. In the next section, we’ll be discussing what this means for business. Working capital of 153,472.81 means the coffee shop has positive working capital and puts the business in a great position to grow. Their current liabilities equal £34,776.83 Working capital is your current assets minus your current liabilities. Working capital, as I explained earlier, is actually a pretty simple equation to get your head around. They both use the same figures, but current ratio divides whereas working capital subtracts. The current ratio is also a different formula to working capital.
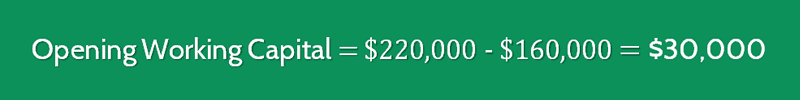
Comparatively, working capital is an absolute amount. The current ratio is expressed, as the name suggests, as a ratio.

The current ratio is a way for investors to weigh up the risk in the business, it is calculated by taking the current assets and dividing them by the current liabilities. They often include taxes, wages payable, accounts payable etc.Īn indicator of a business’ ability to pay these debts is known as the current ratio. Typically they must be able to be converted into cash within one year to be classified as “current”.Ĭurrent assets include but are not limited to:Īccounts receivable (money owed by customers)Ĭurrent liabilities are monies that a company will owe within one year, making them short term debts. What are current assets?Ĭurrent assets are reserves or property of the business that can easily be exchanged for cash, or are already realised as cash or cash-equivalents. Let’s start with a quick recap of current assets and liabilities. And finally, what impact your industry has on your working capital.What positive and negative working capital mean for a business.How to calculate working capital with an example.What current assets & current liabilities are.When investors and CFOs are inspecting a business’ health and level of risk, this is one of the metrics they’ll look at closely. The value of your working capital highlights whether you have enough liquid assets to pay off short term debts. However, as we’ll see, this isn’t a great situation to be in. Working capital can be positive or negative, as your current assets can be lower than your current liabilities. This is done by subtracting your current assets from your current liabilities. Working capital is the value left over after all of your short term debts have been met by your available sources of cash or cash equivalents. However, working capital is actually pretty simple to understand once you break it down. Ah, working capital, another financial term that mystifies many – positive and negative working capital can seem overwhelming but we’re here to make it easier.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
